Overview of Typical Filter Sets
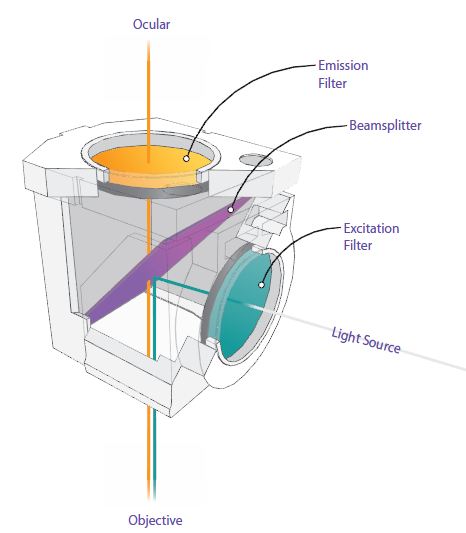
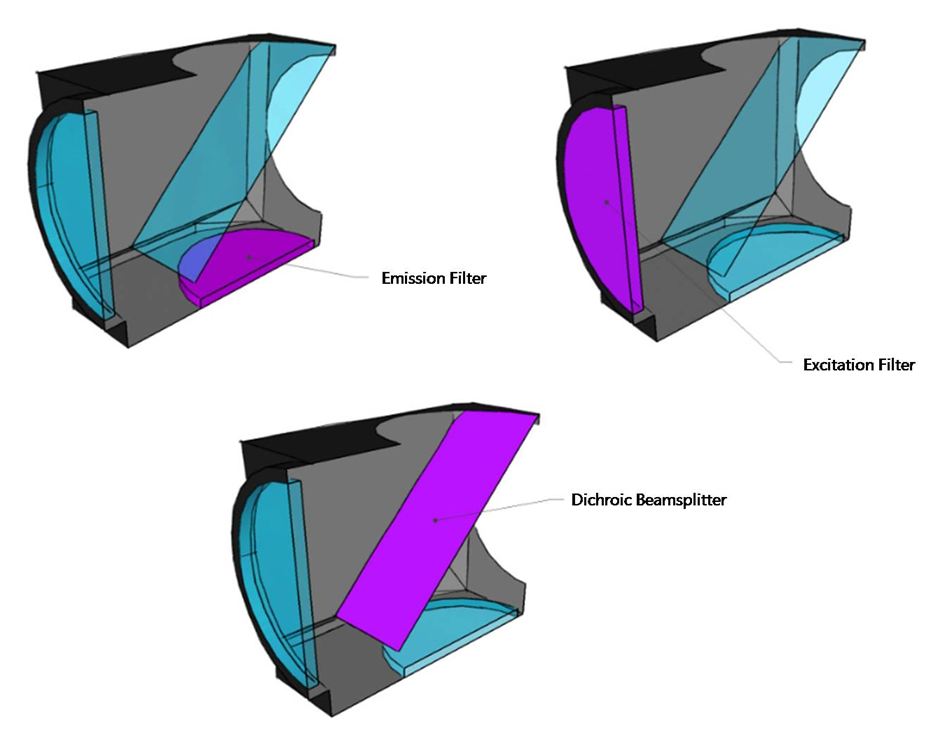
The excitation filter (also called the exciter) transmits only those wavelengths of the illumination light that efficiently excite a specific dye. The emission filter (barrier filter or emitter) attenuates all of the light transmitted by the excitation filter and very efficiently transmits any fluorescence emitted by the specimen. The dichroic beamsplitter (dichroic mirror or dichromatic beamsplitter) is a thin piece of coated glass set at a 45-degree angle to the optical path of the microscope.
Schematic of Typical Filter Cube
The schematic of a typical filter cube for an inverted microscope is illustrated like below.
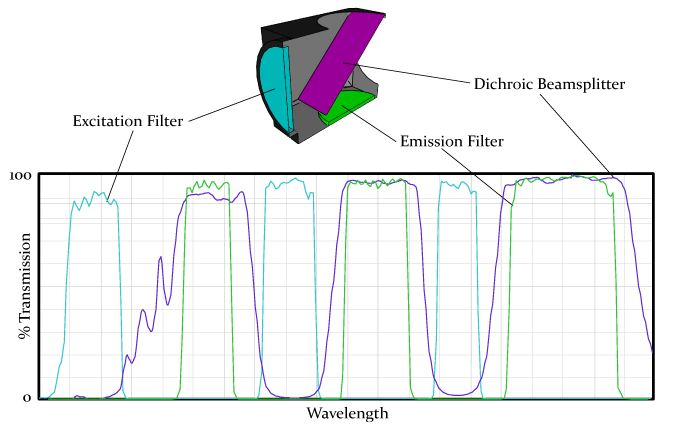
Multi Band Filter Set
One filter configuration is a set including a multi band exciter, multi band dichroic, and multi band emission filter. Each filter can be created to selectively transmit and block multiple bands of wavelengths.
This configuration requires the user to use a color CCD camera and simultaneously capture multiple fluorochromes present in a sample with a single image.
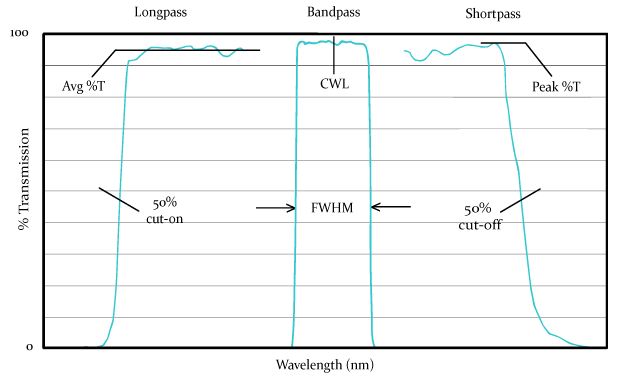
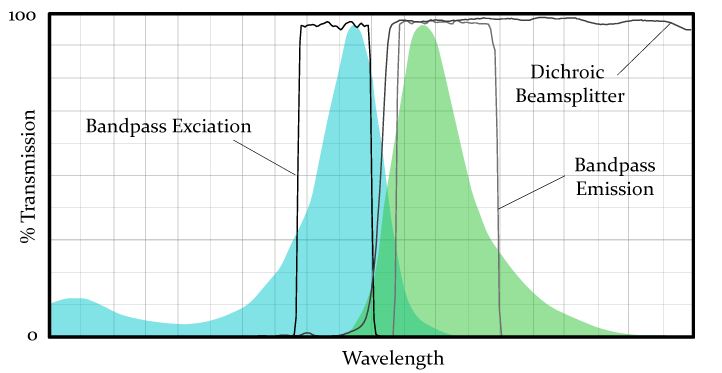
Filter Characteristics
- Bandpass filters are designed to transmit a specific range of wavelengths and block light on either side of that range by their center wavelength and bandwidth.
- LP and SP filters are denoted by their cut-on or cut-off wavelengths at 50% of peak transmission. LP or SP filters that have a very sharp slope.
- Neutral Density (ND) filter blocks all wavelengths of light evenly.
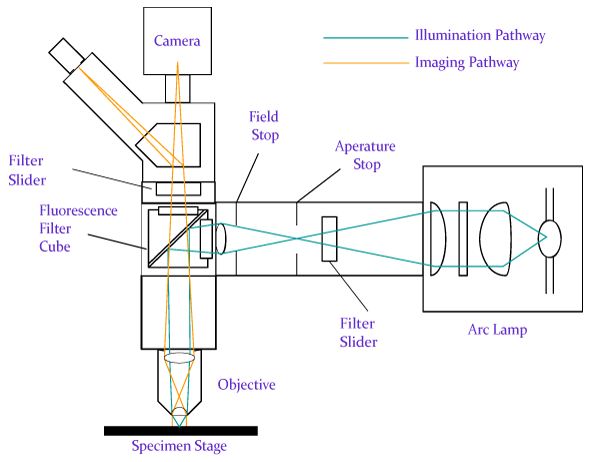
Fluorescence Microscope
This image is a schematic diagram of a typical fluorescence microscope, which uses incident-light illumination. This is the most common type of fluorescence microscope. Its most important feature is that by illuminating
with incident light it need only filter out excitation light scattering back from the specimen or reflecting from glass surfaces.